In the fast-paced world of digital media, the MP4 file format stands out as a cornerstone for video creators and editors alike. With its efficient compression capabilities and broad compatibility across platforms, MP4 allows professionals to deliver high-quality content without sacrificing performance. However, navigating the intricacies of this format can be daunting for newcomers, making it essential to understand its benefits and limitations to maximize its potential.
For those eager to dive deeper into the world of MP4 and enhance their video projects, we invite you to explore the wealth of tutorials and insights available at the VidQuickly Blog. As the premier resource for downloading videos from Facebook, YouTube, TikTok, Instagram, and more, VidQuickly is your go-to destination for mastering the art of video creation and distribution.

Introduction
What is MP4
MP4, or MPEG-4 Part 14, is a digital multimedia container format used to store video, audio, subtitles, and images. It is widely supported across devices and platforms due to its efficient compression and high-quality playback, making it ideal for streaming and sharing content online.
Overview of MP4
MP4: The Lowdown on the Ultimate Video Format
MP4, or MPEG-4 Part 14, is the go-to video format for most people today. It’s a digital container that can hold video, audio, subtitles, and images, making it super versatile. Whether you’re watching a movie, sharing clips on Instagram, or editing your latest vlog, MP4 has you covered.

One of the best things about MP4 is its balance between quality and file size. You get crystal clear HD video without taking up all your storage space. Plus, it’s compatible with pretty much every device and media player out there.
For those looking to download YouTube videos in MP4 format, check out VidQuickly’s YouTube Video Downloader. It’s a quick and easy way to save your favorite videos for offline viewing.
History of MP4
MP4, also known as MPEG-4 Part 14, has evolved significantly since its inception:

Origins and Development
- QuickTime Base: MP4 is based on Apple’s QuickTime File Format. It was standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as ISO/IEC 14496-12.
- Initial Release: The first MP4 specification was published in 2001 (ISO/IEC 14496-1:2001).
- Revisions: In 2003, it was revised and replaced by MPEG-4 Part 14 (ISO/IEC 14496-14:2003), known as MP4 version 2.
Generalization and Extensions
- ISO Base Media File Format: In 2004, MP4 was generalized into the ISO Base Media File Format (ISO/IEC 14496-12:2004), forming the basis for various other formats like 3GP and Motion JPEG 2000.
- Further Development: Subsequent updates and revisions continued to enhance MP4’s capabilities, accommodating new codecs and advanced streaming technologies.
Usage and Impact
- Widespread Adoption: MP4 became a standard for video and audio distribution due to its efficiency and compatibility.
- Technology Integration: It supported a range of applications from mobile phones (3GP, 3G2) to professional broadcasting (DVB File Format).
MP4’s evolution from QuickTime roots to becoming a universal multimedia format highlights its adaptability and enduring relevance in digital media.
>>> Read more: Exploring YouTube’s Key Features and Benefits
Uses of MP4 Format
The MP4 file format is incredibly versatile, widely used for various applications due to its ability to handle multiple types of media efficiently.

1. Video Storage and Playback
MP4 is primarily used for storing video content. It is the preferred format for:
- Movies and TV Shows: Streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video use this Video Format to deliver high-quality video content to users.
- Music Videos: Platforms like YouTube and Vimeo utilize MP4 for music videos due to its efficient compression and high-quality output.
- Personal Videos: Users often record and store personal videos in MP4 format on smartphones and cameras for easy playback and sharing.
2. Online Streaming
MP4 is highly compatible with streaming protocols, making it ideal for online video playback. Its features include:
- Adaptive Streaming: MP4 supports adaptive bitrate streaming, which allows the video quality to adjust based on the viewer’s internet connection. This ensures smooth playback without buffering, even on slower connections.
- Compatibility with Browsers: Most web browsers support this Video Format, allowing users to stream videos directly without the need for additional plugins or software.
3. Multimedia Applications
MP4 can store various types of multimedia content, making it suitable for:
- Educational Content: Online courses and tutorials often use MP4 for video lectures, ensuring that students can access high-quality educational materials.
- Corporate Training Videos: Businesses use MP4 for training and onboarding videos, as the format is widely supported across devices and platforms.
4. Video Editing
MP4 is commonly used in professional video editing workflows. Many video editing software applications, such as Adobe Premiere Pro and Final Cut Pro, support importing and exporting in MP4 format. This makes it easy for editors to work with high-quality footage while maintaining reasonable file sizes.
5. Subtitle Support
MP4 files can include subtitle tracks, which enhance accessibility and provide options for viewers who speak different languages. This feature is crucial for:
- Global Content Distribution: Content creators can reach international audiences by including subtitles in multiple languages.
- Accessibility: Subtitles make videos accessible to individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing, ensuring that everyone can enjoy the content.
6. Mobile Compatibility
Given its efficient compression and high-quality output, MP4 is the go-to format for mobile devices. Most smartphones and tablets support MP4 playback, allowing users to watch videos on the go without compatibility issues. This has made this Video Format the standard format for mobile video applications and social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok.
7. Social Media Sharing
MP4 is widely used for sharing videos on social media platforms due to its balance between quality and file size. Users can upload this Video Format to platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Snapchat without worrying about excessive loading times or quality loss.
Extensions and Variants
MP4 is a versatile container format with several extensions and variants tailored for specific uses. Here’s a deep dive into the key extensions and their applications:
Key Extensions
- .mp4:
- Standard Use: General video and audio storage.
- Application: Widely used across various platforms and devices for both playback and streaming.
- .m4a:
- Audio Files: Used primarily for audio-only files.
- Quality: Commonly used for music tracks and podcasts due to its support for high-quality sound.
- .m4p:
- Protected Content: Encrypted audio files, typically from services like iTunes.
- DRM: Incorporates FairPlay Digital Rights Management.
- .m4b:
- Audiobooks and Podcasts: Contains additional metadata such as chapter markers.
- Features: Allows for features like bookmarking, making it ideal for long audio content.
- .m4r:
- Ringtones: Specifically used for iPhone ringtones.
- Functionality: Same as .m4a but recognized by iPhones as ringtone files.
- .m4v:
- Video Files: Sometimes used for raw MPEG-4 video streams.
- Usage: Often seen in video content purchased from iTunes, supporting both DRM and non-DRM content.
Variants and Related Formats
- 3GP and 3G2:
- Mobile Compatibility: Designed for 3G mobile phones.
- Formats: 3GP for GSM-based phones and 3G2 for CDMA-based phones.
- Features: Support for lower-resolution video and various audio codecs tailored for mobile devices.
- Motion JPEG 2000 (.mj2):
- High-Quality Video: Uses JPEG 2000 video compression.
- Applications: Ideal for high-quality, low-latency video applications.
- DVB File Format (.dvb):
- Broadcasting: Used for storing DVB (Digital Video Broadcasting) services.
- Flexibility: Can store audio, video, and other content using various encapsulation methods.
- MPEG-21 File Format (.m21, .mp21):
- Digital Items: Supports complex digital items, integrating various multimedia elements.
- Usage: Suitable for multimedia applications requiring comprehensive media integration.
Understanding these extensions and variants enhances the versatility of this Video Format, ensuring compatibility across different devices and applications. Whether it’s for general use, high-quality audio, protected content, or specialized mobile formats, MP4 has a solution.
MP4 File Format Specifications
File Structure
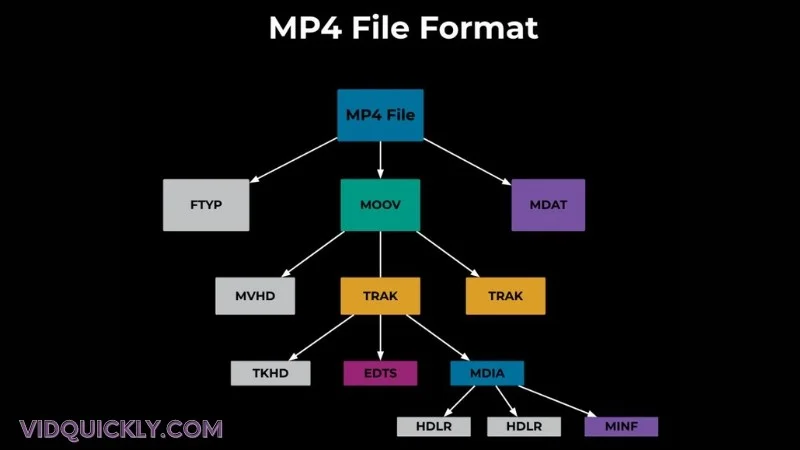
When you’re working with MP4s, think of these boxes as individual containers for different types of data. Each box has its own type identifier and length, kinda like a folder system on your computer, but cooler.
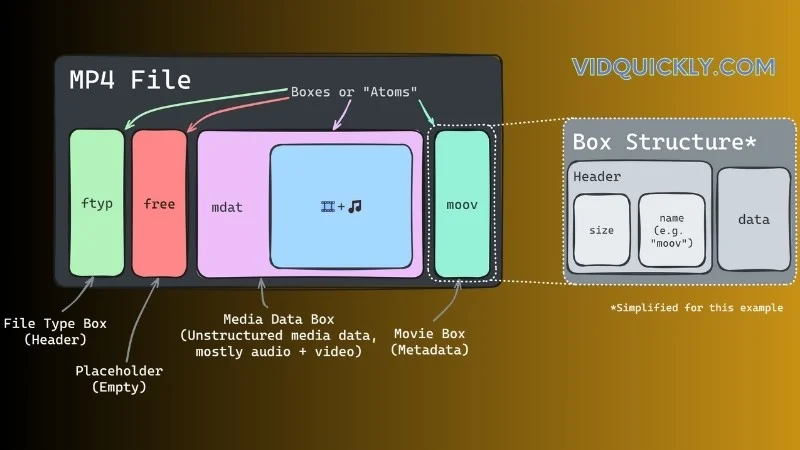
The Basics of Boxes
- Structure and Composition:
- Every bit of data in an MP4 file is stored in these “boxes.”
- They’re like little building blocks that make up the whole file.
- Object-Oriented Magic:
- MP4 files are broken down into these basic objects (or boxes).
- The type of each box tells you what kind of data it holds.
- Types of Boxes:
- ftyp: File type box that indicates the MP4 format version.
- moov: Movie box containing metadata like timing and structure.
- mdat: Media data box where the actual audio, video, and other data live.
- free: Free space box, acting like a buffer or placeholder.
How It Works
- ftyp (File Type Box): This box at the start of the file declares the file type and compatibility, ensuring that media players know what to do with it.
- moov (Movie Box): The moov box is crucial for indexing. It has details about tracks, duration, and timescale.
- mdat (Media Data Box): This is where the magic happens. It contains the actual video, audio, and other media data.
File Type Box (ftyp)
This little box is the key to letting your media player know what’s inside this Video Format.
Think of the ftyp box as the MP4’s ID card, showing what version it is and what it’s compatible with. It sits right at the start of the file, setting the stage for everything that follows.
The Basics
- Purpose:
- The ftyp box declares the file type and ensures compatibility with media players.
- It helps the player understand how to handle the data inside the MP4.
- Structure:
- Major Brand: Indicates the primary use or version of the MP4 file (e.g.,
mp42for MP4 version 2). - Minor Version: A 4-byte integer showing the minor version of the major brand.
- Compatible Brands: Lists other specifications the file complies with (e.g.,
isom,avc1).
- Major Brand: Indicates the primary use or version of the MP4 file (e.g.,
Examples
- Major Brands:
mp41for MP4 version 1mp42for MP4 version 2
- Compatible Brands:
isomfor ISO Base Media File Formatavc1for files containing H.264 video
Understanding the ftyp box is crucial for editing and ensuring your videos play smoothly across different platforms.
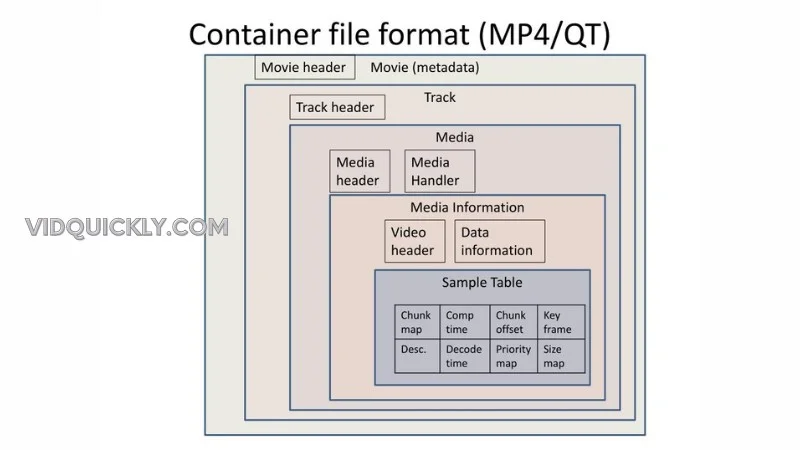
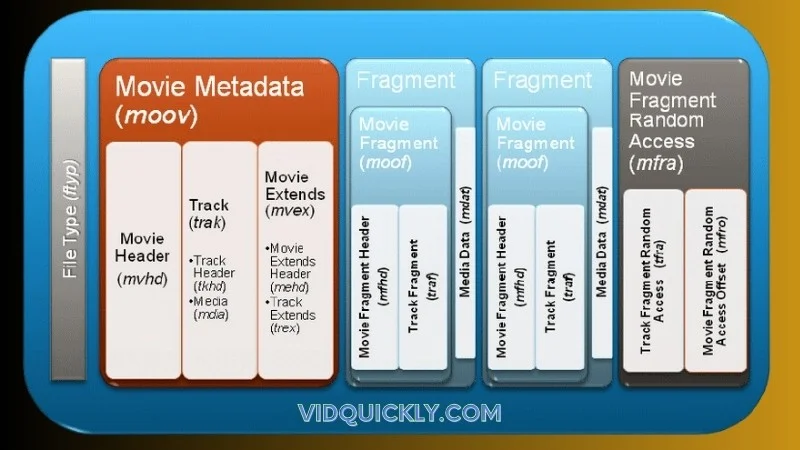
Metadata and Moov Atom
Metadata and the moov atom are the MVPs of your MP4 files, ensuring your video plays smoothly and efficiently, whether you’re streaming or downloading.
Metadata: The Secret Sauce for Streaming
Metadata is like the cheat sheet for your MP4 file. It’s a bunch of data that provides essential information about your video, like the resolution, frame rate, and even the display orientation. Think of it as the “how-to” guide for media players, helping them understand exactly what they’re dealing with.
When you’re streaming your videos, metadata is crucial because it ensures your content plays back seamlessly on all kinds of devices and platforms. It’s the glue that holds everything together, making sure your video looks and sounds on-point no matter where it’s being viewed.
The Moov Atom: The Brain of Your MP4 File
The moov atom is where all the metadata magic happens. It’s like the control center for your MP4 file, containing all the essential information that media players need to know. Inside the moov atom, you’ll find details about your video’s tracks, including the duration, dimensions, and codecs used. It’s the brains behind the operation, making sure everything runs smoothly.
When you’re streaming your videos, the moov atom is a game-changer because it allows media players to start playing your content before the entire file has been downloaded. This is known as progressive download, and it’s a lifesaver for impatient viewers (let’s be real, who isn’t impatient these days?).
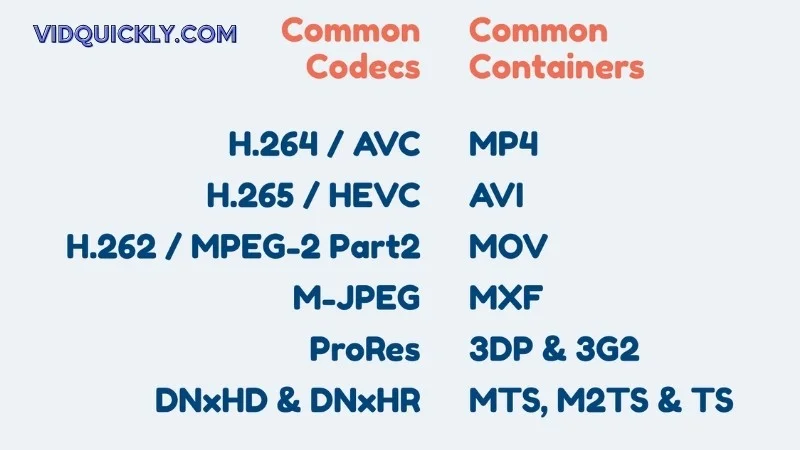
Supported Codecs
Video Codecs
So, you’ve got your MP4 file, but what’s under the hood? Let’s talk video codecs. These bad boys compress and decompress your video files, making them smaller and easier to manage without sacrificing quality.

Video codecs are the tech behind your video files, ensuring they look great and play smoothly. This Video Format supports a range of codecs to keep your content top-notch.
The Basics
- H.264/AVC:
- Popularity: Most commonly used codec.
- Quality: Delivers high-quality video at lower bitrates.
- H.265/HEVC:
- Efficiency: Better compression than H.264, meaning smaller files with the same quality.
- Future-Proof: Ideal for 4K and HD content.
- MPEG-4 Part 2:
- Legacy Codec: Older, but still in use for some applications.
- Compatibility: Works well with a wide range of devices.
- AV1:
- Newcomer: Open-source and royalty-free.
- Compression: Excellent quality and compression, optimized for the web.
Choosing the right codec affects file size, quality, and playback compatibility. Knowing which codec to use can make your video editing and sharing experience smoother.
Audio Codecs
An audio codec (short for “coder-decoder”) is a technology that compresses and decompresses audio data. Think of it as the translator that helps your sound data communicate effectively with media players. In this Video Format, a variety of audio codecs can be used to ensure your audio sounds great while keeping file sizes manageable.

The Main Audio Codecs in MP4
- AAC (Advanced Audio Coding):
- This is the go-to codec for most MP4 files. AAC delivers high-quality audio at lower bit rates compared to older codecs like MP3, making it perfect for streaming and downloading. If you want your music or dialogue to sound crisp and clear without taking up too much space, AAC is your best friend.
- MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer III):
- While AAC is the preferred codec for MP4, you’ll still find MP3 in the mix. It’s widely supported and great for music tracks, but it doesn’t compress audio as efficiently as AAC. If you’re working with legacy content or just want to keep it classic, MP3 is a solid choice.
- MPEG-1 Audio Layer II (MP2):
- This codec is less common these days but still pops up in some Video Format files, especially in broadcasting. It offers decent quality and is often used in professional audio applications.
- ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec):
- If you’re all about preserving audio quality, ALAC is the way to go. This codec compresses audio without losing any quality, making it perfect for audiophiles who want their music to sound exactly as it was recorded.
- Opus:
- A newer codec that’s gaining traction, Opus is designed for high-quality audio streaming, especially for voice and music. It’s super efficient and can adapt to different bit rates, making it great for live streaming and online communication.
Why Audio Codecs Matter
Choosing the right audio codec for your MP4 files is crucial for several reasons:
- Quality vs. Size: Different codecs offer varying levels of compression, which affects the quality and size of your audio. If you want to maintain high fidelity while keeping file sizes down, AAC is often the best choice.
- Compatibility: Not all codecs are supported by every device or platform. If you want your videos to be accessible to a wide audience, you need to choose codecs that are widely compatible, like AAC and MP3.
- Streaming Performance: For creators who share content online, the codec impacts how quickly and smoothly audio loads and plays. Efficient codecs like AAC and Opus enhance the listening experience, especially on slower connections.
Subtitles
Let’s dive into how subtitles work in Video Format files. They’re essential for making videos accessible and adding context.
Subtitles in MP4 files ensure that your videos are accessible to a wider audience, including those who are deaf or hard of hearing, and they can also help with language barriers.

Why Subtitles Matter
Subtitles are essential for several reasons:
- Accessibility: They make your videos accessible to people who are deaf or hard of hearing. This inclusivity can significantly widen your audience.
- Language Support: Subtitles allow viewers who speak different languages to enjoy your content. This is especially important for global platforms like YouTube and social media, where diverse audiences come together.
- Enhanced Comprehension: Sometimes, viewers might struggle to catch every word of dialogue due to accents, background noise, or fast-paced speech. Subtitles help clarify the content, ensuring that your message is received loud and clear.
How Subtitles are Stored in MP4
In MP4 files, subtitles are typically stored as part of the file’s structure, allowing them to be synchronized with the video and audio tracks. Here’s how it works:
- Text Tracks: Subtitles are usually included as text tracks within the Video Format file. These tracks can contain various types of subtitle formats, such as:
- MPEG-4 Timed Text (TT): This is the most common format for subtitles in MP4 files. It allows for precise timing and positioning of text on the screen, making it ideal for synchronized viewing.
- 3GPP Timed Text: Similar to MPEG-4 Timed Text, this format is often used in mobile applications and streaming services.
- Integration with Metadata: The subtitles are integrated with the file’s metadata, which is stored in the moov atom. This allows media players to access and display the subtitles at the correct times during playback.
- Multiple Languages: MP4 files can support multiple subtitle tracks, enabling viewers to select their preferred language or subtitle style. This flexibility is crucial for content creators who want to reach a global audience.
Examples of Subtitle Usage
- YouTube Videos: Many creators upload videos with subtitles to enhance accessibility and engagement. YouTube supports multiple subtitle formats, allowing creators to upload their own or use automatic captioning.
- Streaming Services: Platforms like Netflix and Hulu use this Video Format with integrated subtitles to provide viewers with options for different languages and closed captions.
Streaming and Local Playback
Streaming Capabilities
MP4’s streaming capabilities are a game-changer for video delivery, ensuring seamless playback whether you’re watching a live stream or downloading a video.

Streaming Support in MP4
The MP4 file format is designed with streaming in mind. It includes several features that enable seamless video delivery over the internet:
- Hint Tracks: this Video Format can contain hint tracks, which provide information about how to stream the media data over different protocols. These tracks specify the data units to be streamed and how to serve the elementary stream data, ensuring compatibility with various streaming protocols.
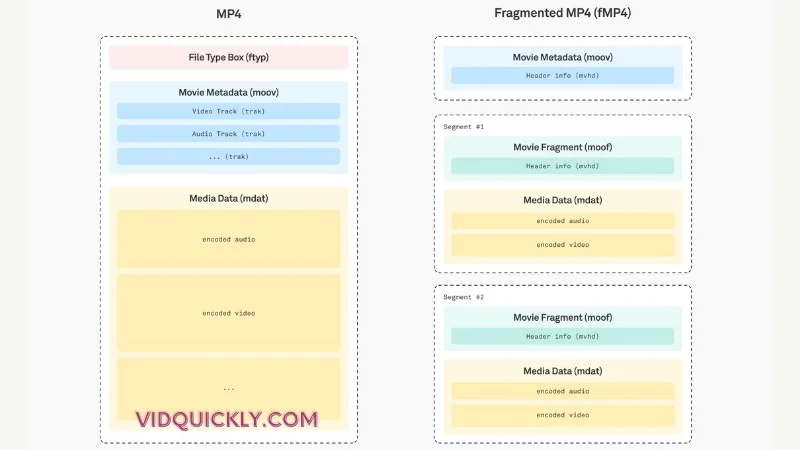
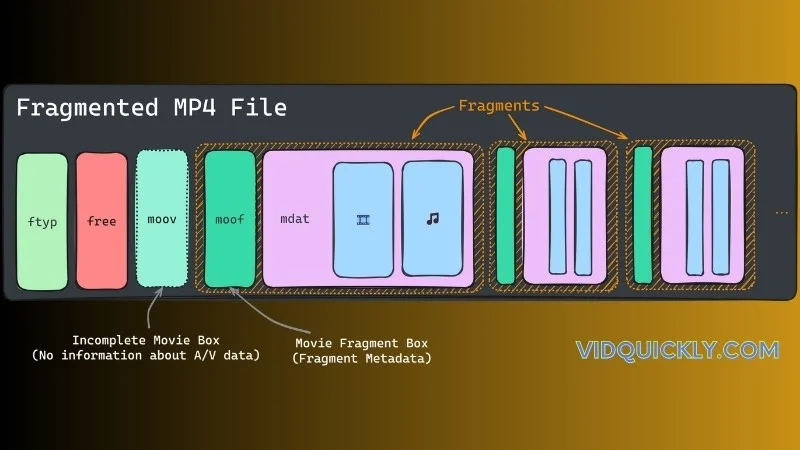
- Fragmented MP4: this Video Format supports fragmented files, which allow the video to be broken down into smaller chunks. This enables progressive downloading and adaptive bitrate streaming, where the viewer can start watching the video before the entire file has been downloaded, and the quality can be adjusted based on network conditions.
- Metadata: The MP4 file format includes metadata, such as the moov atom, which contains essential information about the video, including resolution, frame rate, and codec details. This metadata helps media players understand the video content and ensures smooth playback.
Advantages of MP4 for Streaming

- Compatibility: this Video Format is widely supported across various devices, platforms, and web browsers, making it accessible to a broad audience. This compatibility ensures that your videos can be streamed on a wide range of devices without compatibility issues.
- Compression Efficiency: MP4 uses efficient compression techniques, such as H.264 video encoding and AAC audio encoding, to reduce file sizes while maintaining high-quality video and audio. This compression efficiency is crucial for streaming, as it minimizes bandwidth requirements and ensures smooth playback, even on slower internet connections.
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming: this Video Format supports adaptive bitrate streaming, which allows the video quality to be adjusted based on the viewer’s network conditions. This feature ensures that viewers with slower internet speeds can still enjoy the video without experiencing buffering or interruptions, while those with faster connections can enjoy higher-quality video.
- Live Streaming: MP4 is also suitable for live streaming, as it can be fragmented and delivered in real-time. This makes it a popular choice for live events, gaming streams, and other live content.
Examples of MP4 Streaming in Action
- YouTube: YouTube, the largest video streaming platform, uses MP4 files for both on-demand and live streaming. The platform’s support for this Video Format ensures that videos are accessible to a vast audience across various devices and internet speeds.
- Netflix: Netflix, a leading streaming service, also relies on MP4 files for delivering high-quality video content to its subscribers. The platform’s use of adaptive bitrate streaming, enabled by this Video Format, ensures a seamless viewing experience.
- Social Media Platforms: Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter support MP4 for video uploads and sharing. This allows users to share their content with friends and followers, knowing that it will play back smoothly on various devices.
Local Playback
Local playback ensures your MP4 videos run seamlessly on your device, without needing an internet connection. Perfect for offline viewing.

The Basics
- Hint Tracks Ignored:
- No Network Dependency: Since you’re not streaming, hint tracks are irrelevant.
- Direct Access: The media data is accessed straight from the file.
- Moov Atom Positioning:
- Efficient Playback: Ideally placed at the beginning for quick access, enhancing playback performance.
- Playback Devices:
- Compatibility: Widely supported across smartphones, tablets, laptops, and media players.
- Performance: Optimized for smooth, uninterrupted playback.
Tips for Optimal Local Playback
- Use a Reliable Media Player: While most players support this Video Format, using a versatile player like VLC can enhance your experience with additional features and better performance.
- Keep Your Files Organized: Organizing your MP4 files into folders can make it easier to find and access your videos for playback.
- Check File Integrity: If you encounter playback issues, ensure that the MP4 file is not corrupted. You can do this by trying to play the file on a different device or media player.
Downloading and Converting MP4 Files
Downloading MP4 Files from Various Socials with VidQuickly
Downloading videos from social media can be a hassle, but VidQuickly makes it super easy and efficient. Here’s how you can get your favorite videos from platforms like YouTube, Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok.

VidQuickly lets you download MP4 files from major social media sites quickly and without the need for browser extensions or additional software.
Supported Platforms
VidQuickly supports downloading MP4 files from a wide range of social media platforms, including:
- YouTube
- TikTok
- Vimeo
- Dailymotion
- Twitch
How to Use VidQuickly
Using VidQuickly to download MP4 files from social media is a breeze. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Copy the video URL from the social media platform of your choice.
- Paste the URL into the input field on the VidQuickly website.
- Select the desired video quality and format (MP4) from the available options.
- Click the “Download” button.
- Wait for the download to complete.
That’s it! Your MP4 file will be ready for you to save and enjoy on your device.
Benefits of Using VidQuickly
- Compatibility: VidQuickly works seamlessly across various browsers and devices, ensuring a smooth downloading experience no matter what you’re using.
- High-Quality Downloads: The tool allows you to download videos in high-quality MP4 format, preserving the original resolution and clarity.
- Ease of Use: With its user-friendly interface and straightforward process, VidQuickly makes downloading MP4 files from social media a breeze, even for those who aren’t tech-savvy.
- No Ads or Redirects: Unlike some other video downloading tools, VidQuickly is ad-free and doesn’t redirect you to any third-party websites, ensuring a clean and efficient experience.
Use Cases for Downloaded MP4 Files
- Offline Viewing: Save videos to watch later without an internet connection.
- Sharing: Share downloaded videos with friends, family, or colleagues.
- Editing: Use the MP4 files as source material for video editing projects.
- Archiving: Build a personal library of your favorite social media videos for future reference.
- Backup: Ensure you have a backup of important videos in case they’re removed from the original platform.
Social Media Conversions
Converting videos from social media to MP4 is straightforward with VidQuickly. Here’s a detailed guide on how to do it for Twitter, Facebook, TikTok, and Instagram.
VidQuickly simplifies the process of converting videos from your favorite social media platforms into high-quality files, perfect for offline viewing and sharing.

Step-by-Step Guide
- Twitter to MP4:
- Copy the Tweet URL: Find the tweet with the video and copy its link.
- Convert: Paste the link into VidQuickly and click the convert button to get your MP4 file.
- Facebook to MP4:
- Copy Video Link: Click on the video, select “Copy link”.
- Paste and Convert: Head to VidQuickly, paste the link, and convert it to MP4.
- TikTok to MP4:
- Get the Video URL: Share the TikTok video and copy the link.
- Convert on VidQuickly: Paste the link into VidQuickly for an easy MP4 conversion.
- Instagram to MP4:
- Copy Post Link: Find the video post, click on the three dots, and copy the link.
- Convert: Use VidQuickly to paste and convert it into MP4.
Why VidQuickly?
- User-Friendly Interface: VidQuickly is designed to be intuitive, making the conversion process quick and easy, even for those who aren’t tech-savvy.
- Fast Conversion: The tool is optimized for speed, allowing you to convert videos in just a few moments, so you can get back to enjoying your content without delays.
- No Software Installation Needed: Since VidQuickly is a web-based tool, you don’t need to download any software or apps. Just visit the site, and you’re good to go!
- Supports Multiple Platforms: Whether you’re converting videos from Twitter, Facebook, TikTok, or Instagram, VidQuickly has you covered, making it a versatile solution for all your social media video needs.
Playing MP4 Files
Recommended MP4 players
This Video Format are widely supported, but using the right player ensures the best playback experience. Here are some of the best MP4 players that you should consider.

1. VLC Media Player
Overview: VLC Media Player is a popular open-source media player that supports a wide range of audio and video formats, including this Video Format.
Key Features:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Available on Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS.
- No Codec Packs Needed: VLC comes with built-in codecs, so you don’t have to worry about downloading additional files.
- Advanced Features: Offers options for video filters, subtitle synchronization, and customizable playlists.
Why It’s Great: VLC is known for its versatility and reliability, making it a top choice for anyone looking to play MP4 files without hassle.
2. PotPlayer
Overview: PotPlayer is a lightweight media player for Windows that supports a variety of formats.
Key Features:
- Customizable Interface: Users can tweak the interface to their liking, including skins and layouts.
- High-Quality Playback: Supports 3D video and various video rendering options.
- Built-in Codecs: Like VLC, PotPlayer has a wide range of built-in codecs, eliminating the need for extra installations.
Why It’s Great: PotPlayer is perfect for users who want a highly customizable experience with advanced playback options.
3. QuickTime Player
Overview: QuickTime Player is Apple’s native media player for macOS and iOS, and it supports this Video Format seamlessly.
Key Features:
- User-Friendly Interface: Simple and intuitive design, making it easy to navigate.
- Integration with Apple Ecosystem: Works well with other Apple applications and devices.
- Editing Features: Basic editing tools are available for trimming and combining videos.
Why It’s Great: QuickTime is an excellent choice for Mac users looking for a straightforward player that integrates smoothly with their devices.
4. Windows Media Player
Overview: Windows Media Player is a built-in media player for Windows that supports MP4 playback.
Key Features:
- Easy to Use: Familiar interface for Windows users.
- Library Management: Organizes your media files and allows for easy playlist creation.
- Streaming Capabilities: Supports streaming content from the internet.
Why It’s Great: For Windows users who prefer a simple, no-fuss player, Windows Media Player is a reliable option.

5. MX Player
Overview: MX Player is a popular media player for Android devices that supports a wide range of formats.
Key Features:
- Hardware Acceleration: Offers smooth playback even for high-resolution videos.
- Subtitle Support: Easily add and customize subtitles for your videos.
- Gesture Controls: Intuitive touch controls for volume and brightness adjustments.
Why It’s Great: MX Player is perfect for mobile users who want a powerful and feature-rich player for their MP4 videos.
6. Kodi
Overview: Kodi is an open-source media center that allows you to play and manage your media files.
Key Features:
- Customizable Interface: Users can create their own skins and layouts.
- Add-Ons: Supports a variety of add-ons for streaming and additional features.
- Multi-Platform Support: Available on Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS.
Why It’s Great: Kodi is ideal for users who want a comprehensive media management solution that goes beyond just video playback.
Comparison of popular MP4 players
| Feature/Player | VLC Media Player | PotPlayer | QuickTime Player |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supported Platforms | Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS | Windows | macOS |
| Free/Paid | Free | Free | Free |
| Supported Formats | MP4, AVI, MKV, MOV, FLV, and more | MP4, AVI, MKV, FLV, and more | MP4, MOV, M4V, AVI, and more |
| User Interface | Simple and intuitive | Highly customizable | Clean and straightforward |
| Playback Features | Subtitle support, video filters, playlists | Advanced playback controls, 3D support | Basic editing tools, easy navigation |
| Performance | Excellent playback for high-res videos | Smooth playback with minimal buffering | Good performance for standard videos |
| Additional Features | Streaming capabilities, no ads | Custom skins, built-in codecs | Integration with Apple ecosystem |
| Ideal For | General users, versatile playback | Advanced users, customization lovers | Mac users, basic playback needs |
Compression
Tools and methods for compressing MP4 files
Compressing MP4 files helps in saving storage space and makes sharing videos easier. Let’s explore the best tools and methods for this task.

Why Compress MP4 Files?
- Reduced File Size: Compression significantly reduces the file size of MP4 videos, making them easier to store and share without sacrificing too much quality.
- Faster Uploads and Downloads: Smaller file sizes lead to quicker upload and download times, which is especially important for sharing videos on social media or streaming platforms.
- Improved Streaming Performance: Compressed files require less bandwidth, resulting in smoother playback and reduced buffering during streaming.
Tools for Compressing MP4 Files
- HandBrake
- Overview: HandBrake is a free, open-source video transcoder that allows users to compress and convert video files, including MP4.
- Key Features:
- Supports various codecs (H.264, H.265).
- Customizable settings for resolution, bitrate, and audio quality.
- Batch processing for multiple files.
- Usage: Simply load your MP4 file, select a preset or customize settings, and export the compressed file.
- FFmpeg
- Overview: FFmpeg is a powerful command-line tool for video and audio processing, widely used for compressing MP4 files.
- Key Features:
- Supports a wide range of formats and codecs.
- Allows detailed control over compression settings.
- Can be integrated into scripts for automated processing.
- Usage: Use commands to specify input files, desired codecs, and output settings. For example:bash
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vcodec libx264 -crf 23 output.mp4
- Movavi Video Converter
- Overview: Movavi Video Converter is a user-friendly software that enables easy video compression and conversion.
- Key Features:
- Simple drag-and-drop interface.
- Presets for different devices and platforms.
- Batch conversion capabilities.
- Usage: Add your MP4 file, choose a compression preset, and click “Convert” to save the compressed file.
- Adobe Media Encoder
- Overview: Part of the Adobe Creative Cloud suite, Adobe Media Encoder is a professional tool for encoding and compressing video files.
- Key Features:
- High-quality output with customizable settings.
- Integration with Adobe Premiere Pro and After Effects.
- Supports multiple formats and codecs.
- Usage: Import your MP4 file, choose the desired output format and settings, and render the compressed video.
- Online Compression Tools
- Overview: Various online platforms allow users to compress MP4 files without the need for software installation.
- Examples:
- Clideo: Offers a simple interface for compressing MP4 files online.
- Kapwing: Provides tools for video editing and compression directly in the browser.
- Usage: Upload your MP4 file, adjust compression settings if needed, and download the compressed version.

Methods for Compressing MP4 Files
- Adjusting Bitrate:
- Lowering the bitrate reduces the amount of data processed per second, which decreases file size. However, this can also affect video quality, so finding a balance is key.
- Changing Resolution:
- Reducing the resolution (e.g., from 1080p to 720p) can significantly decrease file size while still maintaining acceptable quality for most viewing scenarios.
- Using Efficient Codecs:
- Switching to more efficient codecs like H.265 (HEVC) can achieve better compression rates compared to older codecs like H.264, allowing for smaller file sizes without a noticeable loss in quality.
- Trimming Unnecessary Footage:
- Removing parts of the video that aren’t needed can also reduce file size. This is especially useful for cutting out intro/outro segments or long pauses.
- Using Two-Pass Encoding:
- This method analyzes the video during the first pass to optimize compression settings for the second pass, resulting in better quality at lower file sizes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using HandBrake for Compressing MP4 Files
Compressing MP4 files with HandBrake can save storage space and make sharing easier. Follow these steps to compress your video files effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Download and Install HandBrake:
- Visit the HandBrake website and download the software.
- Install it on your computer.
- Open HandBrake and Load Your Video:
- Launch HandBrake.
- Click on “File” under the “Source Selection” to open your MP4 file.
- Choose a Preset:
- On the right side, select a preset that suits your needs (e.g., “Fast 720p30” for a balance of quality and size).
- Adjust Output Settings:
- Format: Ensure MP4 is selected.
- Dimensions: Adjust resolution if necessary.
- Filters: Apply filters if needed (optional).
- Video: Set the codec to H.264, adjust the quality slider (lower values = smaller size, but lower quality).
- Set Destination:
- Click on “Browse” to choose the destination folder and name your compressed file.
- Start the Compression:
- Click “Start Encode” to begin the compression process.
By following these steps, you can easily compress MP4 files using HandBrake, balancing quality and file size to suit your needs.
MP4 in Mobile Devices
3GP and 3G2 are multimedia container formats designed for mobile phones, particularly for 3G networks. They are similar to MPEG-4 but tailored for mobile device capabilities.
Key Points
- 3GP:
- Usage: Primarily used on GSM-based (Global System for Mobile Communications) phones.
- File Extensions: .3gp
- Compatibility: Supports video codecs like H.263 and H.264, and audio codecs like AMR-NB and AAC.
- 3G2:
- Usage: Developed for CDMA-based (Code Division Multiple Access) phones.
- File Extensions: .3g2
- Compatibility: Similar to 3GP but also supports EVRC, QCELP, and SMV audio codecs.
- Compatibility with MP4:
- Conversion: 3GP and 3G2 files can be converted to MPEG-4 for better compatibility with modern devices.
- Playback: Many media players and mobile devices support playback of 3GP/3G2 files due to their similarity to MPEG-4.
Today, while some legacy mobile applications may still support 3GP and 3G2 formats, most modern mobile phones and video players prioritize MP4 for its widespread compatibility, better quality, and broader feature set.
Future of MP4
Advancements
MP4 continues to evolve with new codecs and compression methods, ensuring it remains the preferred format for high-quality video streaming and storage.
New Codecs Enhancing MP4
- H.265/HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding):
- Overview: H.265, also known as HEVC, is a successor to H.264 and offers significant improvements in compression efficiency. It allows for the same quality video at about half the bitrate of H.264, making it ideal for streaming high-resolution content like 4K and 8K videos.
- Impact on MP4: With the integration of H.265 into the MP4 format, users can expect smaller file sizes without compromising video quality, which is crucial for mobile devices and bandwidth-limited environments.
- AV1 Codec:
- Overview: AV1 is an open-source codec developed by the Alliance for Open Media. It’s designed to be more efficient than H.265, offering better compression rates and improved quality for streaming.
- Future Potential: As more platforms adopt AV1, MP4 files encoded with this codec could provide even greater efficiency, particularly for streaming services looking to reduce data costs while delivering high-quality video.
- VVC (Versatile Video Coding):
- Overview: VVC is the latest codec standard that promises to outperform H.265 and AV1 in terms of compression efficiency. It is designed for future video applications, including 8K and beyond.
- Long-term Vision: As VVC gains traction, MP4 could evolve to support this codec, allowing for unprecedented video quality at reduced file sizes.
H.266/VVC: The Future of Video Compression
H.266/VVC, or Versatile Video Coding, represents the next generation in video compression technology. It promises significant improvements over its predecessor, H.265/HEVC.

Key Points
- Compression Efficiency:
- Superior Compression: Reduces file sizes by approximately 50% compared to H.265, while maintaining the same quality.
- Storage and Bandwidth: Drastically cuts down on storage requirements and bandwidth usage, making it ideal for 4K, 8K, and high dynamic range (HDR) content.
- Quality and Flexibility:
- Versatility: Supports a wide range of applications, from low-resolution video for mobile devices to high-resolution video for professional broadcasting.
- Enhanced Features: Includes improved motion compensation and advanced coding tools for better visual quality.
- Adoption and Implementation:
- Future-Proofing: As streaming services and broadcasters adopt H.266/VVC, it will set new standards for video quality and efficiency.
- Device Support: Anticipated integration into future hardware and software, ensuring widespread compatibility.
H.266/VVC is set to revolutionize video compression, offering unmatched efficiency and quality, making it a key player in the future of digital media.
Emerging Technologies: How MP4 is adapting to new media trends.
Virtual Reality (VR) and 360-degree Video
As VR and 360-degree video gain popularity, MPEG-4 is rising to the challenge. The format now supports spatial audio, allowing for immersive sound experiences that complement the visuals in VR content.

Additionally, the MPEG-4 specification has been extended to include metadata for describing the projection format and orientation of 360-degree videos, ensuring seamless playback on VR headsets and other devices.
Live Streaming
Live streaming has become a crucial part of modern media consumption, and MPEG-4 is well-equipped to handle this trend. The format supports fragmented MP4 files, which enable adaptive bitrate streaming. This allows live streams to adjust the video quality based on the viewer’s network conditions, ensuring smooth playback even on slower connections.
MP4 also integrates with popular streaming protocols like RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol), making it a natural choice for live streaming platforms and content creators.
High Dynamic Range (HDR) Video
HDR video offers a wider range of colors, deeper blacks, and brighter highlights, resulting in a more realistic and visually stunning image. MPEG-4 has embraced this trend by incorporating support for HDR10, Dolby Vision, and HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma) HDR formats.
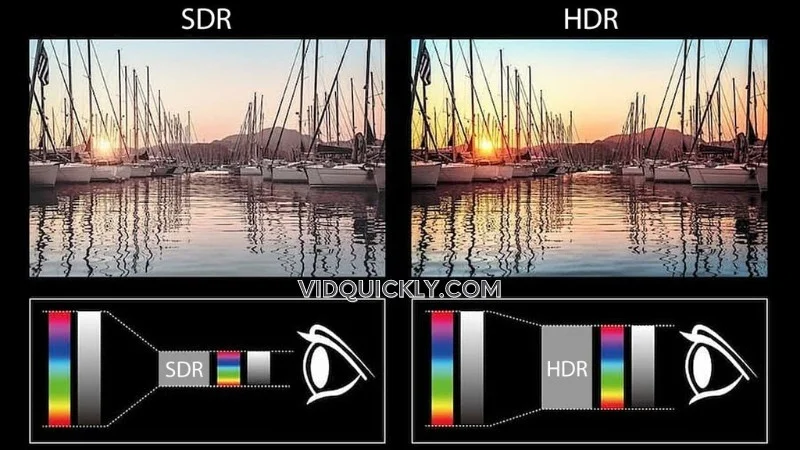

This allows content creators to deliver HDR videos that can be played back on compatible devices, providing viewers with a more immersive and visually appealing experience.
8K and Beyond
As display resolutions continue to increase, MP4 is keeping pace. The format now supports 8K video, which offers four times the resolution of 4K and sixteen times the resolution of 1080p. This allows for incredibly detailed and sharp images, particularly on large screens.
While 8K adoption is still in its early stages, MP4’s support for this high-resolution format ensures it will remain relevant as display technology continues to advance.

Efficient Codecs
One of the key ways MP4 is adapting to new media trends is by incorporating more efficient video codecs. The introduction of codecs like H.265/HEVC (High-Efficiency Video Coding) and AV1 (AOMedia Video 1) has significantly improved compression efficiency, allowing for smaller file sizes without sacrificing quality.
This is particularly important for streaming services, where reducing bandwidth costs is a priority, and for mobile devices with limited storage space.
Conclusion
MP4 stands as a testament to the adaptability and resilience of video formats. From its inception based on the QuickTime File Format to its evolution into a universal multimedia standard, MPEG-4 has consistently met the needs of professional video creators and editors. Its ability to efficiently compress high-quality video and audio while supporting a variety of codecs and applications has made it indispensable in the digital age.
Stay ahead in the world of video technology by exploring more tutorials and news at the VidQuickly Blog, the premier destination for all your video download needs from platforms like Facebook, YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram. Dive deeper and enhance your video creation and editing prowess today!
VidQuickly’s Advice for New Users Downloading MP4 Online from Socials
Choose a Reliable MP4 Downloader
The first step is to select a trustworthy MP4 downloader that supports the social media platforms you use. VidQuickly is a popular choice, as it allows you to download videos from over 1000 websites, including all the major social networks. Look for a tool that is easy to use, fast, and secure.
Copy the Video URL
When you find a video you want to download, copy the URL from your browser’s address bar. This is usually done by right-clicking on the video and selecting “Copy video URL” or “Copy link address.” Make sure you have the full URL, including the “https://” part.
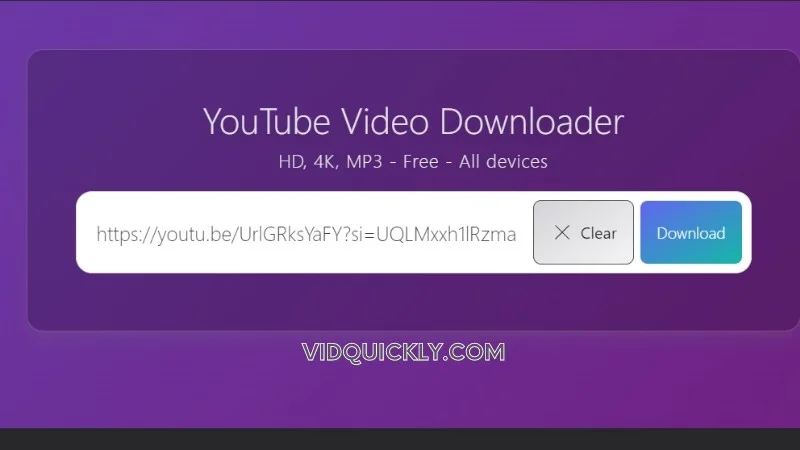
Paste the URL into the Downloader
Open your chosen MP4 downloader, such as VidQuickly, and paste the video URL into the designated field. Some tools may automatically detect the video and provide download options, while others may require you to click a “Download” or “Convert” button.
Select MP4 Format and Quality
Most MP4 downloaders will offer multiple video formats and quality options. Choose “MP4” as the output format, and select the desired resolution (e.g., 480p, 720p, 1080p) based on your preferences and device capabilities. Higher resolutions will result in better quality but larger file sizes.
Download and Save the MP4 File
Once you’ve selected your options, click the “Download” button. The MPEG-4 downloader will fetch the video from the social media platform and save it to your device. Depending on the video length and your internet speed, this may take a few seconds to a couple of minutes.
Enjoy Your Downloaded MP4 Videos
With your MP4 videos downloaded, you can now watch them offline, share them with friends, or use them in your own projects. Remember to follow copyright laws and respect the intellectual property rights of content creators.By following these simple steps and using a reliable tool like VidQuickly, you’ll be able to download MPEG-4 videos from social media with ease. Happy downloading!

FAQs
How to convert MP4 to MP3?
To convert MP4 to MP3, you can use a free online converter like VidQuickly. Upload your MP4 file, select MP3 as the output format, and click “Convert.” Download the MP3 file once the conversion is complete.
How do I save iMovie as MP4?
In iMovie, click on “File” > “Share” > “File…”. Choose your desired settings and ensure “MP4” is selected as the file format. Click “Next,” name your file, and save it to your desired location.
How to compress MP4?
You can compress MP4 files using tools like HandBrake. Open HandBrake, load your MP4 file, choose a preset (e.g., “Fast 720p30”), and adjust settings if necessary. Click “Start Encode” to compress the file.
How to reduce the size of an MP4?
To reduce the size of an MP4 file, lower the bitrate, adjust the resolution, or use a more efficient codec like H.265. Tools like HandBrake or VidQuickly can help you make these adjustments easily.
Can you send MP4 files on Discord using a PC?
Yes, you can send MP4 files on Discord using a PC. Simply drag and drop the MP4 file into the chat window, or click on the “+” button next to the chat bar, select “Upload a File,” and choose your MP4 file to share.

